Gajapati district came into being with effect from 2nd October 1992. Prior to this it was a part (Sub-Division) of Ganjam district. This district lies between 18.450 East to 19.400 West latitude and 85.480 North to 84.270 South longitude. Ganjam district and Andhra Pradesh bound this district on the east, Rayagada district on the west, Ganjam and Phulbani districts on the north and Andhra Pradesh on the south. While the Ganjam is a developed, well connect with road and rail facilities, industrially and agriculturally prosperous district the Gajapati district continue to be an under developed mountainous region, pre dominated by tribal people with low literacy rate and with very low standard of living of majority of people.
What is Gajapati District of Odisha famous for?
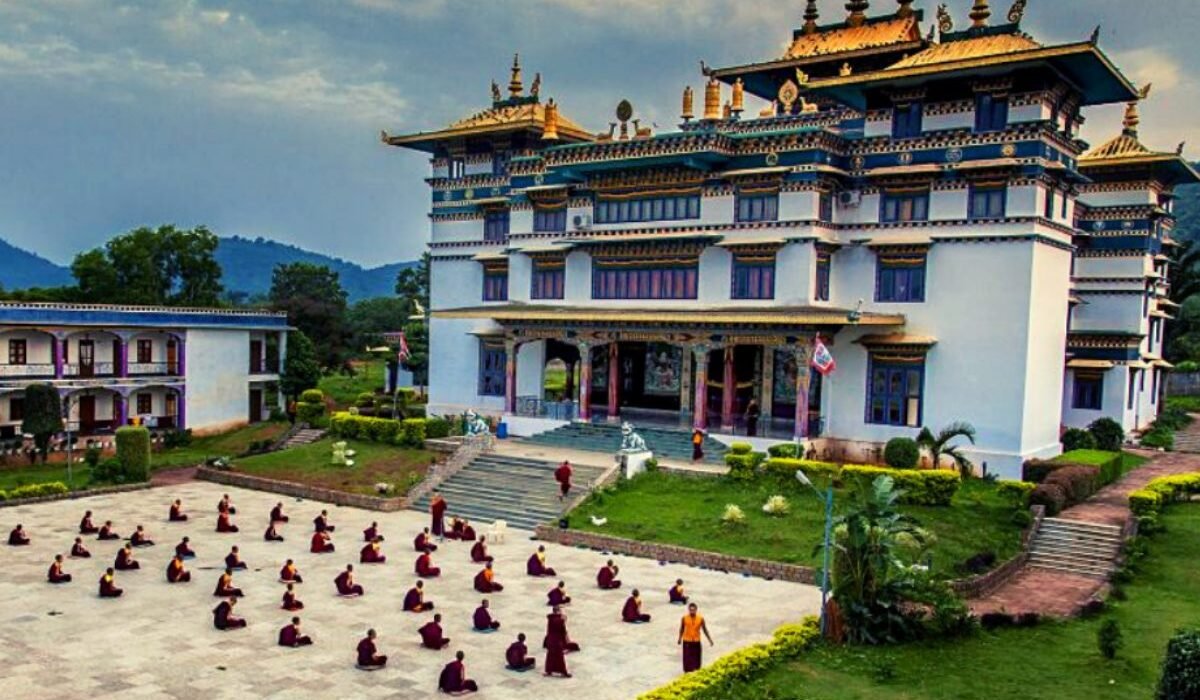
Gajapati District of Odisha is famous for its breathtaking mountainous landscapes, including the majestic Mahendragiri peak (4,923 ft), the second-highest in Odisha. It is a culturally rich region predominantly inhabited by indigenous Soura (Lanjia Saora) tribes, known for their unique ikat textiles, art, and traditions. Formed on October 2, 1992, this serene district offers stunning views, ancient temples, and a cool climate, making it a nature lover’s paradise in southern Odisha.
Geographical Crown:
Home to the towering Mahendragiri mountain, a significant peak in the Eastern Ghats and a revered pilgrimage site.
Cultural Identity:
A predominantly tribal district, renowned as the homeland of the Soura (Lanjia Saora) community and their vibrant culture.
Natural Haven:
Characterized by a cool, hilly climate with great potential for horticulture, featuring diverse soil types from clay loam to red soil.
Key Attractions:
The ancient Maa Tarini Temple at Mahendragiri, serene waterfalls like Duduma, and panoramic hill viewpoints.
Historical & Geographical Profile:
Carved out of Ganjam district in 1992, Gajapati’s identity is defined by its dramatic, undulating topography. Unlike its more developed coastal neighbor, Gajapati is a secluded highland realm where the mighty Mahendragiri peak stands as a natural and spiritual sentinel. The district’s complex geology—with formations ranging from ancient igneous rocks to newer alluvial soils—creates a unique environment perfect for horticulture, with over 60% of its land ideal for plantation crops amidst its cool, mist-clad hills.
Tribal Heritage & Local Life:
The soul of Gajapati beats in its tribal villages. The district is a stronghold of the Soura (Lanjia Saora) tribe, recognized for their remarkable resilience and distinct cultural markers, such as intricate body tattoos and unique wall paintings. Their renowned ikat weaving produces textiles with bold geometric patterns. Life here is intimately connected to the mountains and forests, with traditions and daily rhythms that offer a profound glimpse into Odisha’s indigenous heritage, standing in contrast to more urbanized coastal lifestyles.
Places of Attraction :-
Mahendragiri Hill and Maa Tarini Temple:
This sacred mountain is the district’s premier attraction. The climb or drive up offers breathtaking vistas, culminating at the ancient Maa Tarini Temple, a highly revered Shakti Peetha. The site is a powerful blend of natural grandeur and deep spirituality, especially vibrant during festivals, and its cool, refreshing climate provides a welcome escape.
Duduma Waterfall:
Located on the Machkund River along the Odisha-Andhra Pradesh border, Duduma is one of the state’s most impressive waterfalls. The river plunges from a great height, creating a thunderous cascade amidst dense forests. It’s a spectacular spot for nature photography and feeling the raw power of the region’s pristine landscape.
Tribal Villages of the Lanjia Saora:
For an authentic cultural immersion, visiting a Saora village is a must. These communities, often perched on hill slopes, are known for their unique traditional houses adorned with beautiful wall murals that depict daily life and spiritual beliefs. Interacting with the locals offers an unforgettable insight into their sustainable way of life, art, and warm hospitality.
Serene Hill Stations and Viewpoints:
The district’s rugged terrain is dotted with numerous unnamed viewpoints along its winding roads. Places around Mohana and Gumma offer stunning panoramas of rolling hills, deep valleys, and terraced farms. These spots are perfect for a quiet picnic, meditation, or simply soaking in the tranquil beauty of the Eastern Ghats, far from the crowds.
Climate & Rainfall
Atmospheric temperature varies between 16 to 480 Celsius. The normal rainfall received in the district is 1323.55 mm.
Soil & Rock
The major part of the district belongs to hilly terrain and undulated topography, which is inhabited by the tribals. The highest mountain of the district Mahendragiri lies at an altitude of 4,923 feet above the sea level. The geographical formation of the district is Alluvial, brown land Lateriates, Gondowanas, Newer Dolerites and Archon comprising igneous and metamorphic rocks. The main soil types are clay loam, sandy loam and red soil.
Vegetation
The soil and climate is suitable for plantation crops and there is a great potential of horticulture development in the district. More than 60% of lands are situated in hilly terrain, which has been treated as highlands, which is mainly suited for horticulture plantation and another cultivable land belongs to the category of medium lands (20%) and lowlands(15%).

Leave feedback about this
You must be logged in to post a comment.